Building an Embedded App on YouCan
This guide will walk you through the process of creating and deploying an embedded app within the YouCan platform. We'll focus on building an app that displays orders and sends SMS alerts when a new order is placed. We'll use the YouCan CLI's starter template to streamline the development process.
App Overview
The purpose of this app is to enhance the seller experience. It listens for new order notifications via webhooks and alerts the seller through SMS. The app's backend handles webhook events, while the frontend displays order information.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this tutorial, you'll be able to:
- Build and integrate embedded apps for YouCan.
- Set up your development environment.
- Authenticate your app with the YouCan platform
- Use YouCan APIs for data integration.
- Implement real-time SMS notifications using Twilio.
Requirements
To start building our app, we'll need to set up our working environment first.
- Create a YouCan Partner Account and set a development store.
- Ensure Required Software: You must have NodeJs, a package manager (either npm or pnpm), and git installed.
- Familiarity with JavaScript: To get you started, YouCan provides an app template based on Nuxt.
- Select a Code Editor for managing the codebase.
Let’s Get Started!
Initialize The Project
When we're building a YouCan app, we don't need to install YouCan CLI globally. Instead, these packages should be added as dependencies of our app.
Run the following command using pnpm to install all the dependencies needed - including YouCan CLI itself.
pnpm create @youcan/app@latestor you can use npm
npm init @youcan/app@latest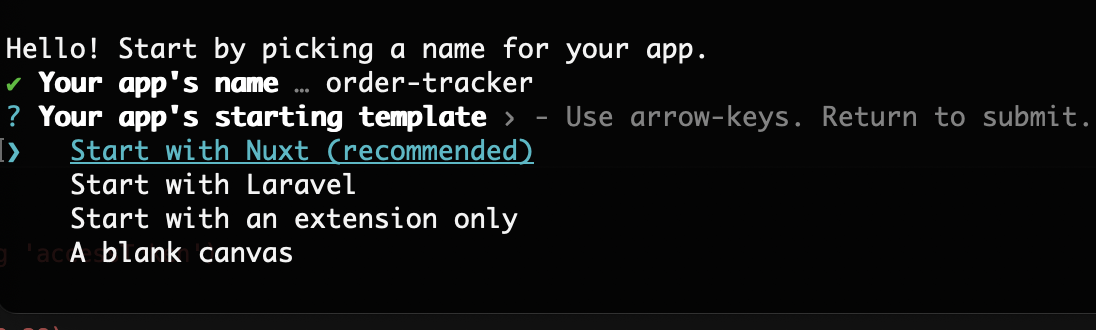
After initialization, choose a name for this app that reflects its purpose. For this example, let's name it "order-tracker".
Next, select the “Start with Nuxt” option as a starting template.
Set Up the Application
The setup process will place all necessary files in the app's directory.
- Let's navigate to our newly created app's directory:
cd order-tracker- Inside the app's directory, we'll make sure all dependencies are installed using
pnpm:
pnpm installThis command installs all the required dependencies listed in the package.json file.
App Structure
As a starting point, the generated app's directory includes a Nuxt template with some preset configurations. Let's see what each folder and file does:
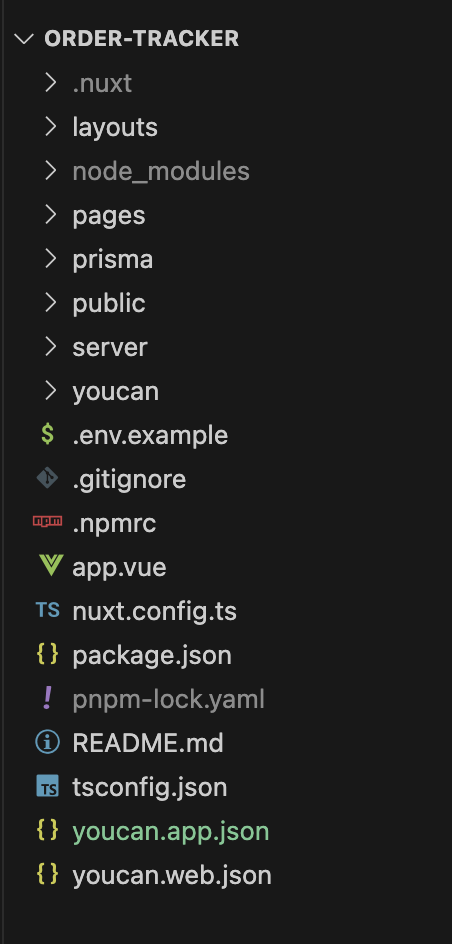
layouts: Defines the structure of our app's UI.pages: Vue components that correspond to the routes of our app.index.vueis the default landing page.prisma: Contains Prisma schema and migration files, used to define and manage the app's database models.public: Static assets like images and fonts go here.server: server-side logic is defined here, including API routes and middlewareyoucan: This directory is specific to the YouCan platform that contains custom configurations and code that interfaces with YouCan APIs.app.vue: The main Vue component that acts as the entry point for our app..envand.env.example: Environment configuration files. During local development, the YouCan CLI handles environment variables automatically for you, but these files are useful if you need to set up other services. You can also runyoucan app env showto display your app's variables for production deployment.youcan.app.jsonandyoucan.web.json: Configuration files specific to our app, such as app name. You generally don't need to manually configure OAuth credentials here as the CLI manages them.
Start the Development Server
We'll get our development server up by running the following command in our app's directory:
pnpm devThis command initiates our app's local development server. If you haven't logged in to your YouCan development store yet, the YouCan CLI will prompt you for authentication.
Authentication and Environment Configuration
Once the server is up and running, we'll have to establish a secure session and authenticate our app with the YouCan platform.
The YouCan CLI's app template simplifies this process with a pre-configured OAuth flow, but you can dive deeper into customization by checking the Authentication Setup Process.
App Settings
When running a local server (e.g port 3000), we must make it publicly accessible for features like Webhooks to work correctly.
1. Making Our Local Server Public:
- We'll use ngrok to expose our local server, providing us with a public URL for receiving webhooks from YouCan.
ngrok http 3000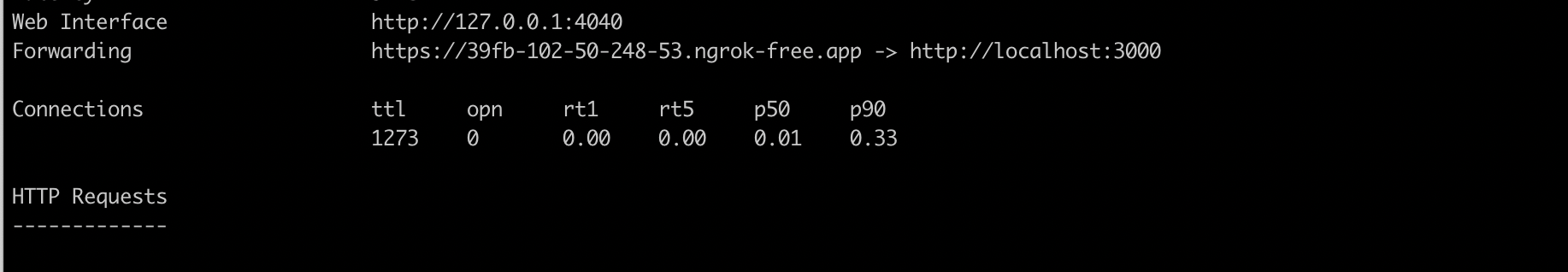
2. Accessing Environment Variables: The YouCan CLI automatically injects all necessary environment variables (like NUXT_YOUCAN_API_KEY, NUXT_YOUCAN_API_SECRET, and NUXT_YOUCAN_API_REDIRECT) when you run pnpm dev. You do not need to manually configure a .env file or youcan.app.json during development.
If you are preparing to deploy to production and need to see your app's environment variables, you can run:
youcan app env showThis will output the configuration values so you can securely set them in your production hosting environment.
By following these steps, we'll have a secure, authenticated app ready to be installed on our development store.
Install the App on a Development Store
To see our app in action, we need to install it on our development store. While your development server (pnpm dev) is running, simply press P in your terminal.
YouCan prompts us to authorize the app within our development store.
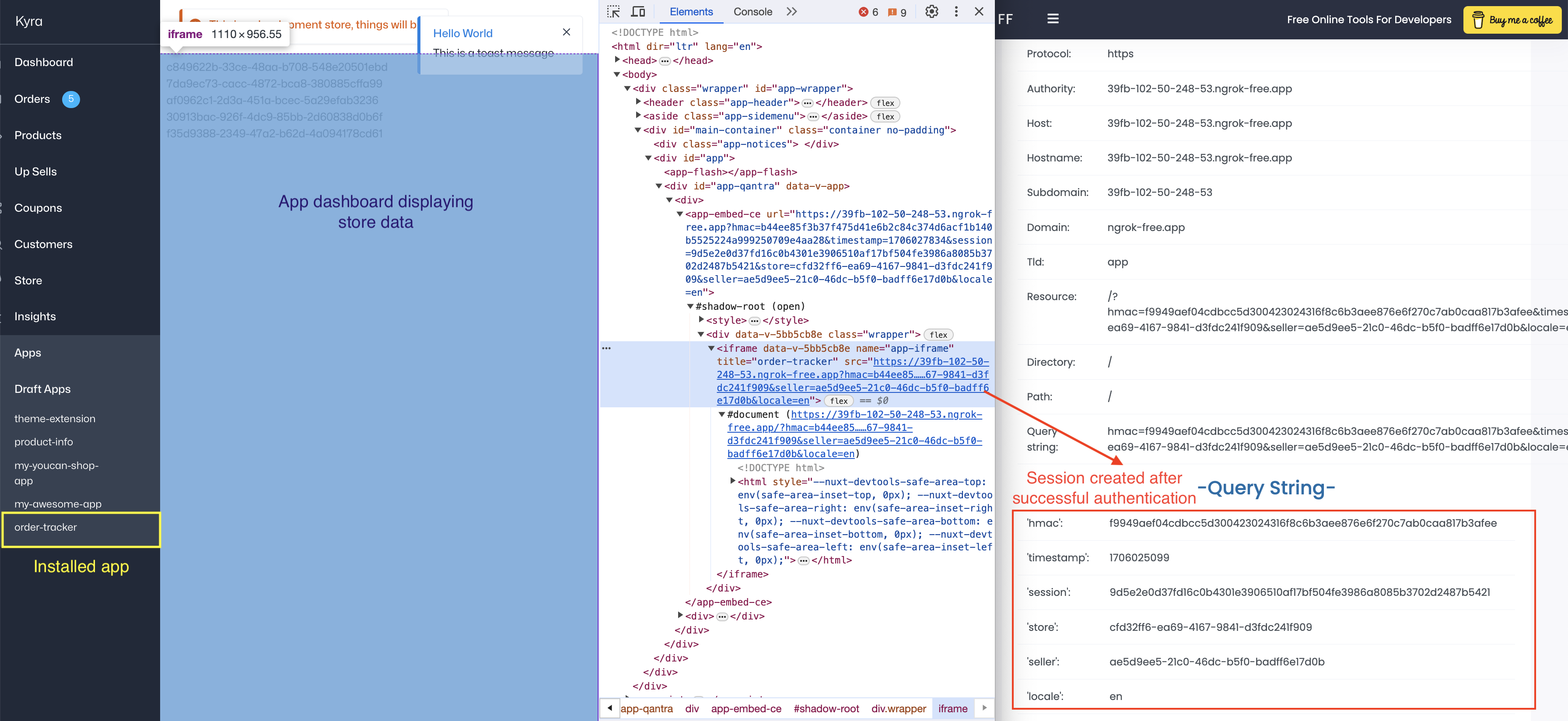
Verify the App Installation and Authentication
Once our app is installed, we'll be able to see it within the YouCan seller-area dashboard. We'll verify that everything is set up correctly by using a URL parser to inspect the callback URL for essential authentication elements, it should include the following:
hmac: A hash of all the request params using our OAuth client secret.timestamp: It shows when the request was made.session: The user's session ID.store: The store ID within YouCan.seller: A unique ID for the seller's account on YouCan.
App Dashboard Implementation
To display orders from the YouCan store in our app, we implement a Vue component for the front end and a server route to handle data fetching.
Frontend
In the index.vue file located in the pages directory, we use the useFetch API to request order data from our backend:
// pages/index.vue
<script setup lang="ts">
const {data: orders} = useFetch<{data: Record<string, {id:string}>}>('/orders');
if (process.client) {
useQantra().toast.show({
title: "Hello World",
description: "This is a toast message"
});
}
</script>
<template>
<div v-for="order in orders?.data">
{{ order.id }}
</div>
</template>
<style>
html {
background-color: white;
font: var(--text-sm-regular);
}
</style>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
This component fetches and displays the id of each order.
Backend: Server Route
We create a server route to query the YouCan API for order data, using the session's access token for authorization.
// server/routes/orders.ts
export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => {
const session = event.context.session;
const response = await fetch('https://api.youcan.shop/orders', {
headers: {
Authorization: 'Bearer ' + session.accessToken
}
});
const orders = await response.json();
return orders;
});2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
WARNING
While the documentation lists https://api.youcan.shop as the API Base URL, for local development purposes, switch to using https://api.youcan.shop. Post app approval, revert to the documented URL for production deployment.
Webhook Logic and SMS Notifications
After displaying orders on the dashboard, we’ll focus on how to integrate webhook handling for real-time notifications and set up SMS alerts for new orders.
Understanding Webhooks
Webhooks are notifications sent by YouCan to OAuth client when an event occur on a store. In our case, YouCan sends a webhook to our "Order Tracker" app when a new order is created.
Refer to the REST Hooks documentation to see the available events.
Webhook Flow
Here's how our app handles a webhook:
- Webhook Triggered: When a new order is placed on YouCan, it triggers a
order.createwebhook event. - App Receives Webhook: Our app's server listens for this event.
- Process and Respond: Once the webhook is received, the app processes the order details then sends an SMS alert.
Set Up Webhooks
To register a webhook, we need to make a POST request to the YouCan API. This is typically done in the callback.get.ts file within our server's routes directory. Here's how to register a webhook for the order.create event:
// callback.get.ts
// ... Your existing code
const r = await fetch('https://api.youcan.shop/resthooks/subscribe', {
method: "POST",
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${access_token}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
target_url: process.env.YOUCAN_WEBHOOK_URL,
event: 'order.create',
})
});2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Implement Webhook Handling
In the app's server logic, we set up a route specifically to listen for and handle incoming webhooks:
// server/routes/youcan/webhooks.ts
export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => {
const body = await readBody(event);
console.log('Webhook processed:', body);
await sendSMS();
});2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
In this code snippet:
readBody(event)parses the incoming webhook request to extract its content.- We check if the event is
order.createand proceed to callsendSMS.
Integrate SMS Notification with Webhook
For the SMS notification functionality, we use Twilio.
- Add the Twilio SDK to our project
pnpm install twilio- Set Twilio credentials in the
.envfile:
TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID=YourTwilioAccountSID
TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN=YourTwilioAuthToken2
- Implement the
sendSMSfunction:
import twilio from 'twilio';
const accountSid = process.env.TWILIO_ACCOUNT_SID;
const authToken = process.env.TWILIO_AUTH_TOKEN;
const client = twilio(accountSid, authToken);
async function sendSMS() {
try {
const message = await client.messages.create({
body: 'New order received',
from: '+12404665161',
to: '+212600600600'
});
console.log('SMS sent:', message.sid);
return message.sid;
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error sending SMS:', error);
throw error;
}
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
With this setup, whenever a new order is created, our app will send an SMS notification, making the seller aware of the new order in real-time.
Testing and Validation
After setting up the webhook and SMS notifications, let's create an order in the YouCan Seller Area dashboard to trigger the webhook.
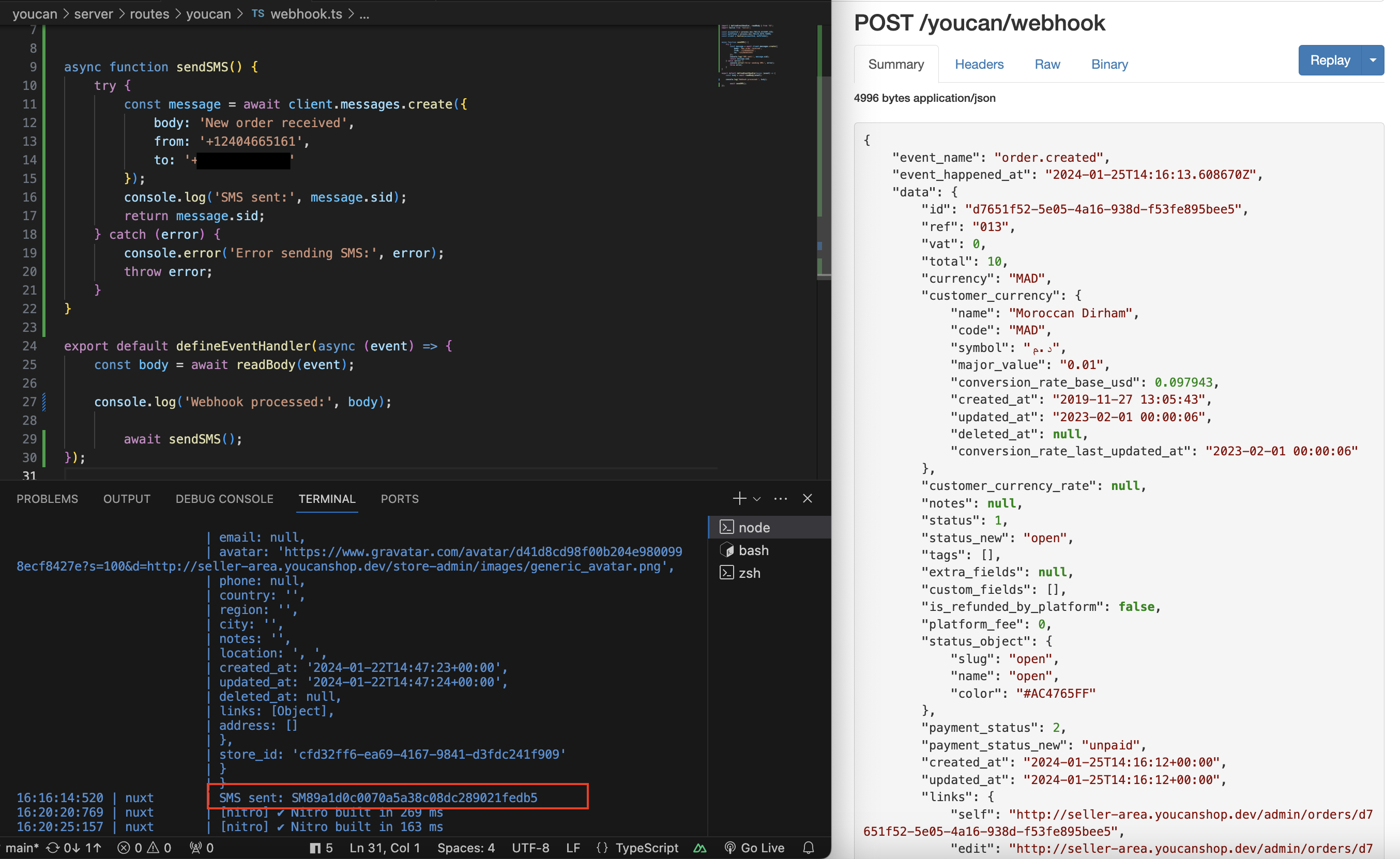
Check our server logs or use tools like ngrok's inspection interface to see incoming
POSTrequests to/youcan/webhook.Verify that these requests contain the order data.
Confirm that the SMS notifications are being sent out.
Customization and Enhancement Opportunities
Note
Before we proceed to the final step of publishing our app, it's important to note that this guide is a basic introduction to the key functionalities of building an app on the YouCan platform. The “Order Tracker” app we created serves as a starting point.
Consider improving the visual appeal and usability of this app with Youcan UI.
For instance, we can refine the order listing by integrating the YouCan UI Table component. Let's see how we can display order's data more clearly, as shown below.
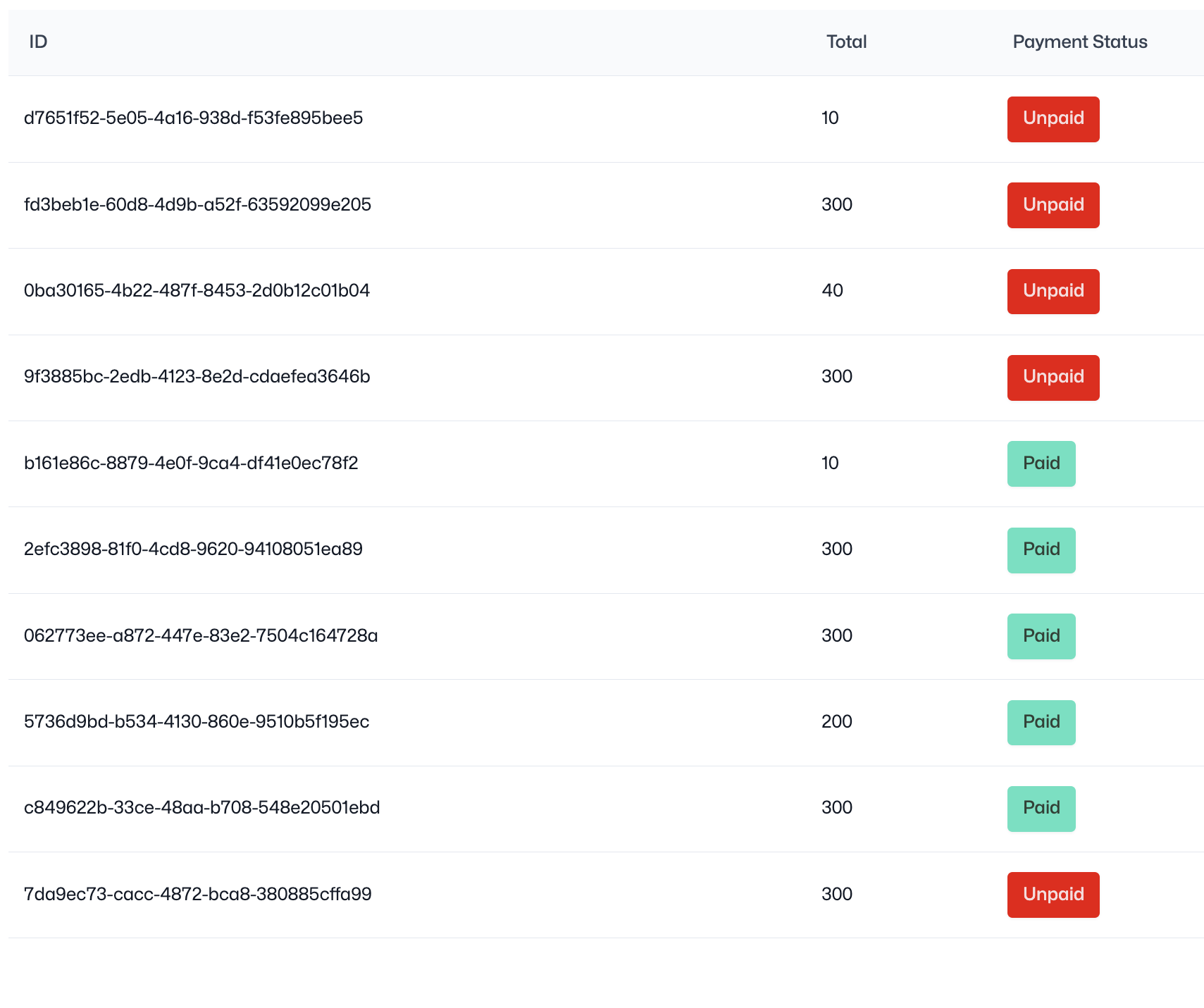
Here's a code snippet demonstrating how Youcan UI can be implemented:
<script setup lang="ts">
import { Table } from '@youcan/ui-vue3';
import type { TableColumn, TableData } from '@youcan/ui-vue3/dist/types/components/Table/types';
import type { StaticStatusDefinition } from '@youcan/ui-vue3/dist/types/components/Status/types';
// Define table columns
const columns: TableColumn[] = [
{ label: 'ID', accessor: 'id' },
{ label: 'Total', accessor: 'total' },
{ label: 'Payment Status', accessor: 'payment_status_new' }
];
// Define status colors
const paymentStatuses: { [status: string]: StaticStatusDefinition } = {
unpaid: {
color: '#EE0200',
label: 'Unpaid',
labelColor: '#f8dcdc',
},
paid: {
color: '#52E2C0',
label: 'Paid',
labelColor: '#2d4236',
}
};
// Fetch orders and transform them into TableData format
const {data: orders} = useFetch('/orders');
const ordersTableData = computed((): TableData[] => {
return orders.value?.data.map(order => ({
row: {
id: order.id,
total: order.total,
payment_status_new: {
variant: 'static-status',
data: {
status: paymentStatuses[order.payment_status_new.toLowerCase()] || {}
},
},
}
}));
});
</script>
<template>
<Table
:columns="columns"
:data="ordersTableData"
/>
</template>
<style>
html {
background-color: white;
font: var(--text-sm-regular);
}
</style>2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
Publish your app
To publish our embedded app, we head to the YouCan partner dashboard, and submit our app for review.
- Navigate to the "Apps" section and locate our app.
- Click on "Push For Review".
- Wait for the YouCan team to review and approve our app.
- Once approved, our app will be published on the YouCan platform, available for any YouCan seller to install.
Important
Please note that after submitting your app for review, the app is locked for changes. It's important to finalize all modifications before submission.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully navigated through the process of creating an embedded app for the YouCan platform. By following these steps, you're now equipped to transform your innovative ideas into functional tools that can enhance the online store experience.